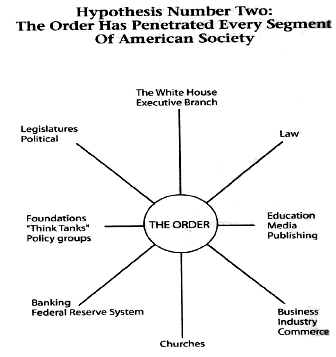
"The North Americans created the myth that those who had wealth or who were children of those of wealth were superior people, harder working, and more intelligent." --H.G. WellsIt seems to be very simple. Accumulate a pile of money. Associate with others who also have piles of money. Network together to combine the money to attain power and control government institutions. Use the government power to keep the wealth within the network. Use the wealth to keep members of the network in power. It all leads to a more orderly business environment. Right?
According to Henry Stimson’s biographer, his father — Dr. Lewis Atterbury Stimson, a surgeon — did not relish the thought of his son’s marriage to a person of a lesser class than his family, even though Mabel’s ancestry, through her grandmother, was directly traceable to Captain Miles Standish of the Plymouth Colony. [9]
 The American health industry has always felt it had a nobler cause than merely making the masses healthy. The motivation of Henry's father, as shown above, was to build a medical infrastructure so that men of his own class could continue to be trained in medical research and the study of disease. In many ways Dr. Stimson had a mentality similar to the doctors in Germany, where had studied. His own classmates would ultimately use Jews as subjects in experiments before World War II, for the "advancement" of knowledge. They, too, simply wanted to know how disease worked in the body and had no regard for persons of lesser class or race. Their ultimate goal was to improve the lot of their own kind. It was the same mentality that pervaded the secret society called Skull and Bones.
The American health industry has always felt it had a nobler cause than merely making the masses healthy. The motivation of Henry's father, as shown above, was to build a medical infrastructure so that men of his own class could continue to be trained in medical research and the study of disease. In many ways Dr. Stimson had a mentality similar to the doctors in Germany, where had studied. His own classmates would ultimately use Jews as subjects in experiments before World War II, for the "advancement" of knowledge. They, too, simply wanted to know how disease worked in the body and had no regard for persons of lesser class or race. Their ultimate goal was to improve the lot of their own kind. It was the same mentality that pervaded the secret society called Skull and Bones.
The Skull and Bones network was illustrated by Antony Sutton in his book, America's Secret Establishment, as follows:
Dr. Lewis A. Stimson
The good doctor
believed that "accumulated wealth" should combine with organized
learning institutions to make their power productive:
"The man, the brain, is the essential. The history of thought and science is filled wίth instances of great accomplishment effected with only the scantiest aid from accumulated wealth; but the same history shows most painfully the cost, the waste, and the limitations due to the lack of that aid. The combination of the two [the brain and wealth] permits the man of affairs to make his accumulated power productive along lines where his interest could not be gratified without the aid of special training, and it makes possible for the possessor of that training, much that could not be accomplished without it. The workshop and the endowment must come from the intelligent interest of the outsider, and that interest must be created and stimulated by the worker.
"Of such fruitful aids to the advancement of knowledge and of wise instruction, this building, for the opening of which we are gathered today, is another added to those grouped upon our Campus which testify to the wise and generous thought of the benefactors of the University. It is for us to use the means thus afforded in order that that wisdom and generosity may have their full effect and that their fruits may stimulate others to effort in the same beneficent work."
 The American health industry has always felt it had a nobler cause than merely making the masses healthy. The motivation of Henry's father, as shown above, was to build a medical infrastructure so that men of his own class could continue to be trained in medical research and the study of disease. In many ways Dr. Stimson had a mentality similar to the doctors in Germany, where had studied. His own classmates would ultimately use Jews as subjects in experiments before World War II, for the "advancement" of knowledge. They, too, simply wanted to know how disease worked in the body and had no regard for persons of lesser class or race. Their ultimate goal was to improve the lot of their own kind. It was the same mentality that pervaded the secret society called Skull and Bones.
The American health industry has always felt it had a nobler cause than merely making the masses healthy. The motivation of Henry's father, as shown above, was to build a medical infrastructure so that men of his own class could continue to be trained in medical research and the study of disease. In many ways Dr. Stimson had a mentality similar to the doctors in Germany, where had studied. His own classmates would ultimately use Jews as subjects in experiments before World War II, for the "advancement" of knowledge. They, too, simply wanted to know how disease worked in the body and had no regard for persons of lesser class or race. Their ultimate goal was to improve the lot of their own kind. It was the same mentality that pervaded the secret society called Skull and Bones.The Skull and Bones network was illustrated by Antony Sutton in his book, America's Secret Establishment, as follows:
Networking Through Marriage
When Henry Lewis Stimson married Mary White, he gained a phenomenal connection to the Order through his new in-laws that tapped into many generations of accumulation of wealth and power in New England. Mary White Stimson's father, Charles Atwood White, and her brothers were not only members of Skull and Bones, but her uncle, Henry Dyer White, was treasurer of the Russell Trust Association in 1856, the year Skull and Bones became a state-chartered corporation in Connecticut.
This strong connection to the Order's goals gave young Stimson a foot in the door with another relative of his wife — Bonesman Sherman Evarts (Yale, Skull and Bones,1881), who became his own law associate — but to a Bonesman who was a Yale classmate of his father (both were members of the Yale class of 1863), William Collins Whitney; while Henry's uncle and namesake, Rev. Henry Albert Stimson (Skull and Bones 1865) was only two years behind the two. [10]
The secret society at Yale soon was able to control — as was its goal, according to Antony Sutton in the video below — the boards of many of the most prestigious networks of professionals in America — attorneys, clergy, universities, and the medical profession.
This strong connection to the Order's goals gave young Stimson a foot in the door with another relative of his wife — Bonesman Sherman Evarts (Yale, Skull and Bones,1881), who became his own law associate — but to a Bonesman who was a Yale classmate of his father (both were members of the Yale class of 1863), William Collins Whitney; while Henry's uncle and namesake, Rev. Henry Albert Stimson (Skull and Bones 1865) was only two years behind the two. [10]
The secret society at Yale soon was able to control — as was its goal, according to Antony Sutton in the video below — the boards of many of the most prestigious networks of professionals in America — attorneys, clergy, universities, and the medical profession.
See Antony Sutton videos.
 |
| Belmonts' mansion in Newport |
Hamilton College had also been the alma mater of Whitney’s father-in-law, Henry B. Payne, before his move to Ohio in 1833. Payne's own father-in-law, Nathan Perry, was the leading merchant in what was then "the West." [11]
Through this marriage, U.S. Senator Henry B. Payne had thus made contact with the nautical Rhode
Island Perrys of Newport — a town with the unpleasant distinction of
having been the center of the African slave trade. [12] Newport was then an opulent resort for America’s most wealthy, including the Vanderbilt and Astor families as well as the Rothschild banking representative August Belmont, who married the daughter of Commodore Matthew Calbraith Perry.
 |
| Nast cartoon of Boss Tweed |
Whitney boasted that he hired Root’s firm because, in so many words, Root knew how to manipulate the law without breaking it. It was a useful lesson for those who wanted to control the increasingly powerful federal government.
Inventing the “Pump and Dump”
Whitney’s
loyalty to the Democrats, however, won him an appointment as Secretary of
the Navy under Grover Cleveland in 1885. As naval chief for four years,
Whitney supervised an ambitious program to build battleships in order to
modernize the navy — to the benefit of the Perry family, who were, incidentally, connected by marriage with Rothschild banking agent, August Belmont, whose financing was critical in the plan. Only by building up the naval fleet of battleships could America have the ability by 1898 to challenge Spain in Cuba and the
Philippines, necessary for the expansionist plans of President Taft's Skull and Bones network. [13] Ship construction on such a massive scale required money, of course, and August Belmont was there to help the Perrys and Whitney — all an intricate part of "the government" of President Cleveland — with the financing of the massive effort.
By
1890 Whitney had returned to New York, and his investment syndicate began
consolidating street railways in Philadelphia, New York, and smaller
cities into one electric transit company. They hired attorney Francis Lynde Stetson to incorporate America’s first holding company, which would become a model for financial fraud even to the present day. [14] Within ten years, the Whitney syndicate would "merge" with the Rockefellers, according to the New York Times story posted to the right.
 |
| Metropolitan Traction |
According to the legal model Stetson followed, stock of Metropolitan Traction Company,
a holding company, was issued to pay Whitney and his associates for the
forty or so independent surface transit companies whose properties they
had purchased, including the right to operate exclusively in various metropolitan areas (called franchise rights). Since Whitney’s syndicate
controlled the new city officials, they were able to obtain a monopoly
concession to build one electric streetcar system along the various
routes previously authorized — a right which theoretically increased the value of the
properties sold to the holding company, even though most of the purchased properties were decrepit horse-car lines in
unprofitable territory, with little earning capacity or value. Still
Metropolitan paid prices in amounts from five to twenty times their
acquisition costs plus anticipated cost of construction. [15]
When
the holding company’s management (Whitney’s wealthy syndicate members who desired to invest in the most modern technology then available) began
declaring huge dividends for Metropolitan Traction Company — thus pumping up the stock’s price to ever greater heights — the unwary public rushed to the NYSE to buy the stock. Insiders who knew how inflated the value was, were happy to dump their stock to the tune of millions in profits for themselves.
Having
once sold all their stock, the promoters then felt no obligation to
actually build the modernized streetcar system they had promised.
Newspaper publicity against the fraud perpetrated by the Metropolitan
Traction Co. resulted in rescission of its monopoly franchise, an action
overturned after an appeal to the Supreme Court handled by Elihu Root's firm.
The evidence supports only one conclusion:
Henry Stimson’s true role as an attorney and “statesman” was engineered by men inside Yale's inner core. His role as Secretary of War placed him in a position of being able to defend financial investments abroad of the men he fronted for. As his network saw it, without continued profits from those companies, stocks and related interests they held, they would be unable to support Yale's endowment, which, as a consequence, would limit the influence in political affairs of their alumni, who had branched out into so many areas of American life. It was a vicious cycle. Whether the money or the power came first was of no consequence; reality was that the loss of either meant the loss of both.
Investment Roll-Overs
This merger of investments, as indicated in the Whitney Syndicate cover-up story above, is highly suspicious. Why would the transportation empire controlled by William C. Whitney and Thomas Fortune Ryan begin this switch in 1900 from electrically powered transportation to oil and gas powered engines?
We can only surmise that part of the answer may have been the fact that 1900's Yale Skull and Bones graduates included a Rockefeller, whose uncle was John D. Rockefeller, and whose first cousin was John D. Rockefeller, Jr. Percy (who went by his middle name "Avery") in 1901 married Isabel Goodrich Stillman, sister of Elsie Stillman. Both were daughters of James Stillman, president of the National City Bank.
Elsie Stillman had married P. Avery's elder brother, William G. Rockefeller in 1898. Perhaps Yale's elite saw an opportunity to benefit its endowment by using this scion as leverage for its own sustenance.
[This subject will be examined at another time. It is also dealt with at other blog/websites of this author: MinorMusings.com and QuixoticJoust.blogspot.com., each of which contains labels and a search engine to facilitate further research.]
Stimson's law office was located
almost adjacent to the site where in 1914 the Federal Reserve Bank of
New York would be located, in a building which would remain his home
base off and on for over fifty years. [16] When Root left the firm in 1899 to join the Republican administration, Stimson and another associate, Bronson Winthrop,
started their own firm in the same location, engaged primarily in
corporate securities and litigation.
 |
| Skull and Bones 1900--Percy Rockefeller, seated at right. |
Winthrop (an American globalist,
who had been born in Paris and educated in England), shared with John Forbes Kerry a mutual ancestor, Wait Winthrop, as detailed in Untitled Aristocracy.
 In
1906 Stimson followed the same path blazed by Elihu Root — as attorney
for the southern district of New York — the district with jurisdiction
over the New York Stock Exchange and the lower Manhattan banks. Bronson
remained in the original offices to carry on the firm’s legal business,
with Stimson returning from time to time between appointments in
Washington. These men comprised an internationalist, even
imperialistic, circle of men deter-mined to make America a supreme power
in the world.
In
1906 Stimson followed the same path blazed by Elihu Root — as attorney
for the southern district of New York — the district with jurisdiction
over the New York Stock Exchange and the lower Manhattan banks. Bronson
remained in the original offices to carry on the firm’s legal business,
with Stimson returning from time to time between appointments in
Washington. These men comprised an internationalist, even
imperialistic, circle of men deter-mined to make America a supreme power
in the world.When Edith Root married Ulysses S. Grant III in 1907, The New York Tribune, then owned by Whitelaw Reid, considered the upcoming nuptials to be something akin to a royal coronation. Three days before the wedding the Sunday insert proclaimed:
Daughter of Secretary of State to Wed Grandson of a President.
Photos of the bride, the groom, Elihu Root, his son, Elihu, Jr., Mrs. Clara Root were presented in a collage, which also included a photo of President Grant's son, General Frederick Dent Grant and wife, Ida Honore Grant and their daughter--Julia Dent, otherwise known as Princess Cantacuzene. Julia, it seems, had married the White Russian Romanov Prince Michel Cantacuzene in 1899 and would live in the Ukraine until the Russian Revolution in 1917 made refugees of them.
Musical Chairs Skull and Bones Style
In
1899 Republican Elihu Root was appointed secretary of war by President
McKinley, who had spearheaded the Spanish-American War, which would then
lead to his suppression of the Boxer Rebellion in China. [17]
Less than six months after the inauguration on his second term,
McKinley was assassinated, and Theodore Roosevelt became President.
Secretary of State John Hay, whose daughter Helen in 1902 would marry
Whitney’s son Payne (Skull and Bones 1898), had supervised the treaty to
end the Spanish-American War and formulated the Open Door policy. [18] No doubt Secretary Hay was looking out for his daughter's financial future in his role as foreign policy adviser to the President--equating what was best for the nation as what was best for Standard Oil, in which Payne Whitney had a huge stake which he inherited from his Bonesman uncle, Oliver Hazard Payne.
When Hay left the Cabinet, Elihu Root took his position and would be replaced in turn by William Howard Taft (Skull and Bones 1878, son of co-founder Alphonso Taft). Taft had first served in 1900 on the Philippine Commission, eventually serving as Governor General of the Islands, before advancing to the chair of Secretary of War in 1904. After his stint as head of the State Department, Taft moved to the White House in 1909.
When Hay left the Cabinet, Elihu Root took his position and would be replaced in turn by William Howard Taft (Skull and Bones 1878, son of co-founder Alphonso Taft). Taft had first served in 1900 on the Philippine Commission, eventually serving as Governor General of the Islands, before advancing to the chair of Secretary of War in 1904. After his stint as head of the State Department, Taft moved to the White House in 1909.
As
President, Taft appointed Root’s former associate Stimson to be
Secretary of War in 1911. In 1912, after Taft and TR had campaigned
against each other, thus making way for a Democrat, Woodrow Wilson, to
usher in the radical banking “reforms” which the Republicans had been
supporting by other names for years, Taft returned to Yale as a
professor until he was named Chief Justice of the Supreme Court in 1921.
In
1927 Stimson served under Calvin Coolidge in Taft’s former role of
Governor General of the Philippines (where John Kerry’s great-uncle W. Cameron Forbes, had also served), as well as being Secretary of State in
the administration of Republican Herbert Hoover. So popular (or perhaps
only “connected”) was Stimson that he was also tapped by Democrats
Franklin Roosevelt and Harry Truman to be Secretary of War. [19]
Stimson’s
ubiquity in each successive administration was due, not so much to his
military and diplomatic brilliance, but to his knowledge of how to
secretly finance war and extract spoils from the defeated — combined with
his closeness to the money spinners operating undeterred behind the
scenes. Colonel Stimson was like a sentry, pacing back and forth in
front of the door to the henhouse where geese were busily laying golden
eggs. He was there, not to protect the geese or their eggs, but to run
interference for his co-conspirators inside who snatched up the gold as
soon as it appeared.
These "geese" represent pools of wealth accumulated through hard work, charitable donations and taxes imposed on Americans. Investment bankers, ostensibly intending only to “borrow” the gold and return it with interest, have been trained for generations how to stealthily remove that gold, in order to amass huge fortunes for themselves through market manipulation and fraud.
These "geese" represent pools of wealth accumulated through hard work, charitable donations and taxes imposed on Americans. Investment bankers, ostensibly intending only to “borrow” the gold and return it with interest, have been trained for generations how to stealthily remove that gold, in order to amass huge fortunes for themselves through market manipulation and fraud.
When
they fail in their claimed intent to return the gold, to prevent
exposure they blithely plan new wars or other diversions in order to
save their reputations. McKinley, Roosevelt and Taft, for example,
promised the American people that there was an urgent need to “liberate”
the islands of Cuba and the Philippines from Spain, and that the
territory would be “developed” and “reconstructed” for the benefit of
those abused populations.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
[9] Godfrey Hodgson, THE COLONEL, p. 48; The Family Forest Descendants of Thomas Mitchell genealogy.
[10]
Stimson had worked since leaving law school for Sherman Evarts, another
Bonesman (1881) from a prestigious, politically connected, family, at
52 Wall Street—the same building which housed National City Bank of New
York, where Franklin Roosevelt would later have his law office.
Sherman’s father was William Maxwell Evarts
(Skull and Bones 1837), the attorney general under Andrew Johnson (who
defended the Republican on impeachment charges) as well as being
secretary of state under Rutherford B. Hayes when the controversy over
the 1876 election was decided). The elder Evarts was also a trustee of
the Peabody Educational Fund, 1867-1901 and a member of the Corporation
of Yale College, 1872-91. See OBITUARY RECORD OF GRADUATES OF YALE UNIVERSITY DECEASED FROM JUKE, 1900, TO JUNE, 1910.
[11]
“Mary Perry was the only daughter of Nathan Perry and Pauline Shimmer.
Nathan had moved to Cleveland in 1804, one year after Ohio became a
state. He became the chief rival of John Jacob Astor in the fur trade,
and later became the leading merchant in Cleveland. Edward Perry, a
Quaker, emigrated to Sandwich, Mass around 1639. Two of his sons, tired
of harassment of Quakers, moved around 1704 to Narragansett country,
near the town of Newport, Rhode Island which had large farms which used
many slaves imported through Newport. Church of England enjoyed greater
prestige. The impact of this gay, opulent, slaveholding society was
unfavorable to the growth of so ascetic a sect as the Quakers, and the
Perrys eventually moved into the Anglican communion. Freeman Perry
married Mercy Hazard in 1755, the daughter of Oliver Hazard. She
inherited 300 acres in North Kingstown and lived and died there.” Oliver Hazard Payne website. The Payne mansion was donated to Marist College, which hosts the website.
[12]
“Rhode Island was a key juncture of the ‘notorious triangle’ in which
Rhode Island rum was sold for African slaves, who then were sold in the
Caribbean for molasses and sugar that were, in turn, sold to rum
distillers in Rhode Island….The papers of other Rhode Islanders with
slave trade connections appear in Part 2. These businessmen lived in
Providence and Newport as well as Bristol, which was a center of the
African trade in later years, until the 1808 congressional ban on slave
importing.” Editorial Adviser: Jay Coughtry, Author of The Notorious Triangle: Rhode Island and the African Slave Trade, 1700–1807.
[13] The battleships Maine and Texas, commissioned during Whitney’s tenure, were useful in the Spanish-American War that began in 1898.
[14]
Originally called Bangs & Stetson, the firm’s name was later
changed to Davis, Polk & Wardwell, though in 1890, while former
President Cleveland was a partner there, it was known as "Bangs,
Stetson, Tracy, & MacVeagh." Partner Charles Tracy was the
father-in-law of J.P. Morgan. Its offices were located at 15 Broad,
next door to the Morgan bank. Bangs made his reputation by taking on
William ‘Boss’ Tweed, whose corrupt political machine dominated New York
City in the 19th century. Stetson was one of the first attorneys to
build a large practice by advising corporations on business matters (as
opposed to litigation). In 1887 Stetson began representing J. Pierpont
Morgan when he helped Morgan combine several small electric companies
into General Electric. The firm had also been counsel for Samuel J.
Tilden in the Tilden-Hayes controversy over the 1876 Presidential
election and also set up the U.S. Steel, International Paper, and ITT
corporations. The Vault Guide to the Top 100 Law Firms, 7th edition,
(2004), p. 122;
The
name “Wardwell” belonged to Stetson’s son-in-law, who was appointed to
the Red Cross Mission to Russia. This mission was discussed by Antony
Sutton in his book , Wall Street and the Bolshevik Revolution.
[15] Hendrick , The Age of Big Business, p. 42; . See also "Taking Panama."
[16] Hodgson states that the firm was on the 14th floor of the Liberty Mutual Insurance Building at 32 Nassau. Godfrey Hodgson, The Colonel, p. 48. Today’s maps do not identify that building, but it appears to have been very near the New York Fed.
[17]
McKinley favored the remonetization of silver. Aware of silver
sentiment among his constituents, he sought some means of securing
bimetallism without inflation and therefore surprisingly voted with the
Democratic majority to pass the Bland-Allison Act of 1878 over the veto
of President Hayes, authorizing limited silver purchases and instructing
the treasury secretary either to coin the silver or to issue silver
certificates. As author of the McKinley Tariff Act in 1890, he forced
tariffs to new highs. He was then defeated for reelection to Congress.
He served as governor during the Panic of 1893, before being nominated
for President. Although McKinley was prepared to campaign on the issue
of tariffs, the nomination of William Jennings Bryan—an ardent
free-silver advocate—changed the central issue of the campaign. McKinley
dropped his advocacy of silver coinage and came out strongly for the
gold standard, winning the support of President Cleveland and many other
conservative Democrats.
[18] Hay carried to the Treaty the protocol issued by McKinley. In the re-election campaign, the Republican Platform
characterized the Spanish-American War as “a war for liberty and human
rights … a war unsought and patiently resisted,” and called Americans to
“a new and noble responsibility” in foreign affairs. The document
reaffirmed the party’s traditional commitments to the gold standard,
tariff protectionism, trade reciprocity, veterans’ pensions, voting
rights for all races, and an inter-oceanic canal in Central America. It
approved the annexation of Hawaii (1898), antitrust legislation, and the
creation of a cabinet-level department of commerce.
[19] Another fascinating Cabinet member during this era was Charles Joseph Bonaparte,
great-nephew of the Emperor Napoleon—first serving as Secretary of the
Navy, and then as Attorney General during Theodore Roosevelt’s
administration. In 1875 Bonaparte, a Baltimore attorney, married Ellen Channing Day, daughter of Bonesman, Thomas Mills Day (1837), in Newport, Rhode Island.